Category: Additional Tests
-

Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate
Indications: This examination can detect, from a biological abnormality noted, inflammatory or infectious syndrome. Principle: The sedimentation rate of red blood cells is affected by many factors, including the electrical charges and the concentration of proteins involved in inflammation. Technique: Sampling 1.6 mL of citrated blood tube (0.4 ml citrate solution to 3.8%), preferably practiced…
-
Transaminases AST and ALT
Indications: This is basically to highlight, thanks to the determination of transaminases SGOT and SGPT, cytolysis, whether liver, smooth muscle origin (eg the heart) or ridged. Principle: Hepatic cytolysis release in plasma enzymes that are normally absent. Technique: Levy of 1 to 2 mL of blood in a dry tube or lithium heparin in a…
-
Serum Calcitonin or Thyrocalcitonin
Indications: Hormonal assay is useful in the diagnosis of medullary thyroid cancer. Principle: Thyrocalcitonin is a 32 amino acid peptide synthesized by the thyroid parafollicular C cells. The rate is dependent on blood levels of ionized calcium, phosphate, magnesium and some hormones gastrin, glucagon, estrogens, histamine. It regulates the mineral metabolism by inhibiting bone resorption…
-

Prothrombin Time and INR (International Normalized Ratio)
Indications: Used to be a bleeding disorder, whether congenital or acquired, examination serves primarily to monitor patients on oral anticoagulant treatment based on anticoagulants. These drugs lower blood clotting by decreasing the synthesis of factors II, VII, IX and X coagulation. This assay is also used to assess liver function in case of failure as…
-
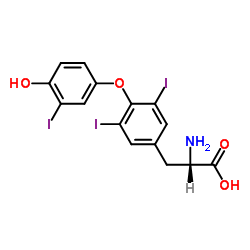
Triiodothyronine
Indications: This is to assess thyroid function, eg detect hyperthyroidism. Principle: T3 is from 80% by deiodination of T4. Some free T3 is present in the normal state in the blood: the majority is a TBG (thyroxine binding globulin). Technique: Sampling 10 mL EDTA blood. Results: Normal values: 0.3 to 0.4 mU / L. Pathological…
-
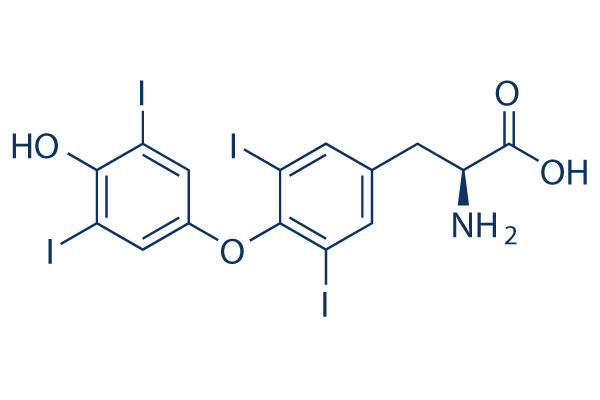
Total thyroxine (T4)
Indications: The review is needed in the suspected diagnosis of hyper- or hypothyroidism. Principle: T4 is the main hormone secreted by the thyroid, the free form is the only active. Technique: Blood Sample EDTA (ethylene diamine tetra-acetic acid). radioimmunoassay or enzyme immunoassay. Results: They went in 1-3 days. Normal values: from 45 to 110 mcg…
-

Sweat Test
Indications: This is to detect in children with cystic fibrosis or cystic fibrosis. Principle: To do this, we must highlight a sweat secretion abnormally rich in sodium chloride. The examination is essentially practical in children. Technique: Formerly, the sweat was collected on a pad placed in the back or the forearm. For sweating, external heating…
-

Spermogram
Indications: This is the first review to humans during the etiological research of infertility. Principle: The review is to examine a semen sample under a microscope after measuring its volume and its physicochemical characteristics. Technique: Semen is collected by masturbation to the lab after 3 or 4 days of abstinence. The collection can be performed…
-

PSA (prostate specific antigen)
Indications: The dosage of the circulating antigen secreted by prostate glandular cells can detect a cancer, to assess the stage to follow the change. Found in any other tissue, its rate is in any prostatic disease: whether adenoma, cancer, or prostate. Principle: Prostatic specific antigen is a glycoprotein secreted by the prostate. Technique: Sampling 5…
-
Proteinuria Bence Jones
Indications: The review is an essential element of research myelomas. Principle: Protein Bence-Jones is a dimer of light chains (kappa or lambda) of immunoglobulins. It is present in the urine in 70% of cases of myeloma. Technique: Thermosoluble, the protein makes the precipitate which appears at 60 ° C is lost at the boil to…
You must be logged in to post a comment.