Category: Additional Tests
-
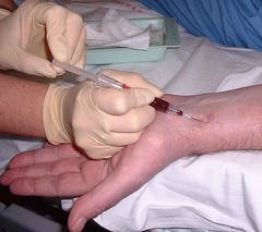
Arterial Blood Gas
Indications: The review used to assess the amount of haematosis in respiratory diseases, whether acute or chronic. Principle: It involves measuring blood pressure O2 and CO2, the bicarbonate ion concentration and arterial blood pH. Technique: Sampling 3 mL of arterial blood via the femoral or radial puncture into a heparinized syringe sealed. It is essential…
-
Gamma Glutamyl Transpeptidase (γ-GT)
Indications: The examination is diagnostic of liver disease and / or chronic alcoholism. Principle: The γ-GT is a membrane glycoprotein that catalyzes the transfer of gamma glutamyl residue glucathion. It is especially in the kidney, pancreas, spleen, intestine and, to a lesser amount, in the heart, the liver, the brain. one dose serum enzyme activity.…
-
Ferritin
Indications: Doser ferritin to estimate the amount of iron stored in the body in the case of anemia or more generally of a chronic fatigue. Principle: Abundant in liver and macrophages, ferritin’s iron storage protein. Mainly intracellular, however, it is present in the plasma, but in small quantities. A correlation exists between ferritin and iron…
-
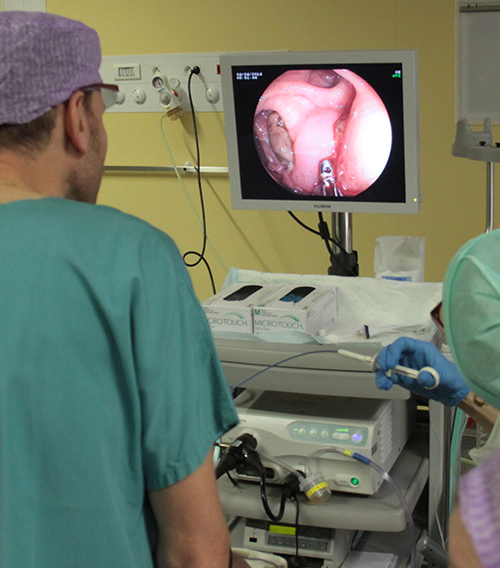
Functional Exploration of Digestion – Test Goiffon
Indications: This examination can detect digestive shortcomings from the analysis of digestion, performed on stool. Principle: It establishes, in this protocol, a microscopic study of food waste, substances of intestinal origin of the fecal flora, stool pH, organic acids and ammonia found in the stool. Technique: Stool sample, sufficient for physicochemical analysis. Results: They are…
-
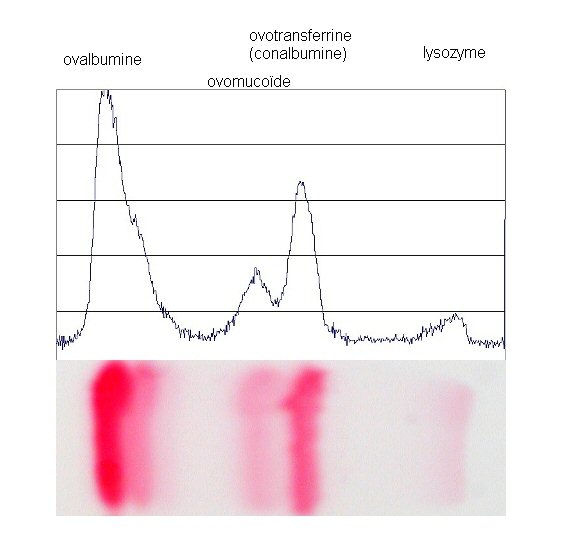
Serum Protein Electrophoresis
Indications: Simple and inexpensive way, this review allows to know the blood composition protide, mainly albumin and globulins. Principle: Albumin is preferentially secreted by the liver, and globulins, by lymphocytes: the dose is therefore a good way to assess the operation of these two sources of production. Placed in a basic medium and in an…
-

Hemoglobin Electrophoresis
Indications: The examination is useful when suspected hemolytic anemia or haematological disease associated with the patient’s geographic origin, namely Africa, specifically the southern Sahara. Principle: The majority of abnormal hemoglobins have a different electric charge from normal: the amino acids of the globin located outside are hydrophilic effect and electrically charged. By subjecting the hemoglobin…
-
Urinalysis (Urine Culture)
Indications: The urine sample to diagnose a urinary tract infection by microscopy and seeding in a Petri dish, and, thanks to the susceptibility to guide the antibiotic treatment. Principle: The collected urine is cultured and counted the observed colonies. Technique: Ideally, the material is taken to the laboratory in the morning, the patient with little…
-
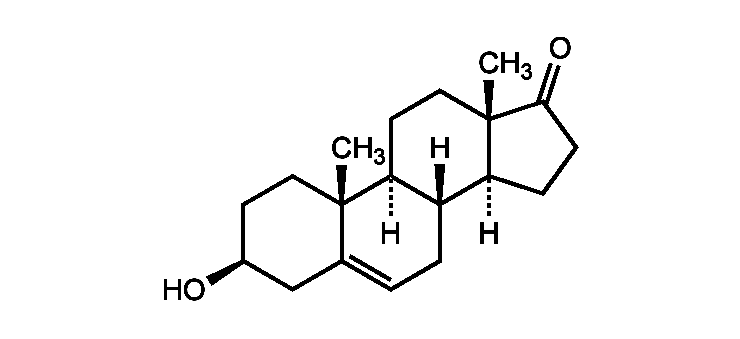
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHA)
Indications: The test is useful for diagnosis of adrenal hyperandrogenism. Before prescribing DHEA, we must ensure that the absence of biological cons-indications; consideration, as far as levels of DHA, help them. Principle: The dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate is a pro-hormone androgen without own activity. Catabolised androgen, it acquires a virilizing action. Its prescription appears to affect sleep…
-
D-dimer
Indications: The dosage of D-dimer is an aid in the diagnosis of venous thrombosis formed, phlebitis as pulmonary embolism. This examination is also useful when in doubt about a diagnosis of disseminated intravascular coagulation. Principle: Degradation product of fibrin, D-dimer in the plasma appears in a non-physiological activation of coagulation. Technique: 5 mL sample of…
-

CRP (C-reactive protein)
Indications: This is to assess and diagnose through a blood test, an inflammatory condition. Principle: This protein synthesized by the liver, is present at low levels in serum normally. Its concentration increases rapidly in case of inflammation. Technique: Levy of 2 mL of blood in a dry tube. Results: Normal values: 5 to 15 mg…
You must be logged in to post a comment.